Graphics from around the world are taking global industries and the commercial sector by storm. In this article, we discuss When Should You Use Vector or Raster Graphics?.
Everywhere you go, you will find some sort of graphical representation making the headlines in the news, on top of advertising banners, as digital backgrounds for various forms of content, and much more.
Perhaps the most practical use of graphics and abstract vector background nowadays is to create eye-candy for targeted audiences, and this grabs their attention spontaneously.
There are multiple principles that constitute the right use of graphics that are being utilized today by companies and organizations to suit their needs expediently. We can categorize them all into two major groups, namely the Raster Graphics and Vector Graphics.
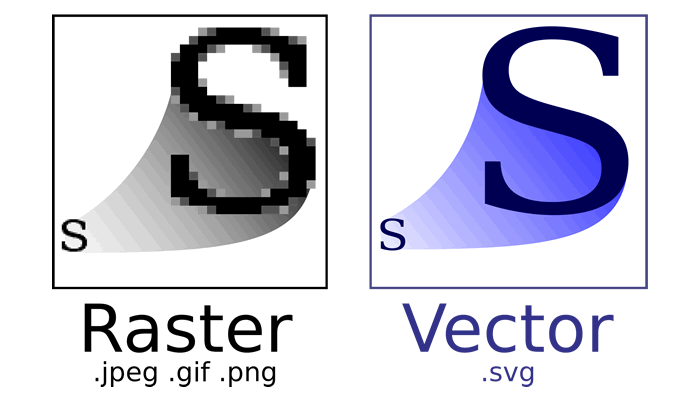
The primary difference between Raster and Vector graphics is that raster graphics are composed of pixels, whereas vector graphics are primarily based on paths or mathematical instructions. The pixel is a picture element represented by a dot, a physical point within the image. There are websites like Freepik where you easily find free vector graphics for your projects.
Take, for example, a ‘selfie’ that you capture on your mobile phone. The picture you snapped is made up of a collection of pixels. On the other hand, in vector graphics, there are mathematical statements or sequential commands that draw the lines and shapes based on the environment, which can range from 2-D to 3-D in nature.
Furthermore, vector graphics are considered best for printing since they can retain their crispiness and image quality regardless of how big or small the output you want them to produce. Now that we have discussed some of their plain and simple attributes, let’s take a look at some of the best uses of each type of graphics.
Table of Contents
Best Use of Raster Graphics
Raster graphics are commonly referred to as a bitmap, which is composed of a matrix of small dots, where each dot can be assigned a different colour. Standard file formats include:
- GIF (graphic interchange format),
- JPG (joint photographic expert group),
- PNG (portable network graphics),
- PSD (Photoshop Document), and finally,
- TIFF (tag image file format).
You can also find raster images in other forms, including PDF (portable document format) and EPS (encapsulated postscript). So far, the best uses of raster graphics include:
· When using Photography
The fact of the matter is that many companies use realistic photographs to lure in customers, possible candidates, and prospects. This consists of the automobile companies putting out their latest model’s image on the cover of car and vehicle magazines.
Unfortunately, vector images fail to bring about the same effect as a raster can. Raster graphic has a more realistic touch to them, and that is why they are commonly used to promote products and services for various restaurants, travel & tourism companies, as well as numerous retail and e-commerce businesses.
· Designing a Website
Next up we have customers and clients who want to improve their websites or build their own. In this case, you would also use raster graphics since they are not only visually appealing, but they can be adequately used for covering the backgrounds.
· Manipulating Images
Lastly, raster images are also useful if what you want is to apply special effects to your captured images. Blur effects will produce a much more softened background as well as make your image at the front pop-out.
The drop shadow effect gives your objects within the image to have a raised effect. This allows you to make a shadow appear within the objected with the help of other effects. For painted or airbrushed appearance, you can use the Feather effect, and lastly, the glow effect casts a shadow on the entire background of the image.
Best Use of Vector Graphics
Now let us focus our attention towards vector graphics, which are images and shapes that are created with the help of points that each have their own ‘x’ and ‘y’ coordinate. Vector files contain pathways that connect these points to develop enclosed shapes with the help of lines. Both are considered mathematical data, and they can be rendered and interpreted by numerous creative tools and browsers.
The most common vector file formats include:
- EPS (encapsulated postscript),
- PDF (portable document format), and
- SVG (scalable vector graphics).
AI also have another vector file format that was introduced by Adobe Illustrator and can only be created or edited using the mentioned software. The best uses of vector graphics include:
· Making Road Signs or Any Signs for that Matter
The thing about signs is that they come in all shapes and sizes. This is why to retain their image quality; you would require a vector image that can help you produce prints for various mediums regardless of how small or big the final copy is.
· Embroidery
Majority of the custom and tailor-made embroidered products are made with the help of software run sewing machines. These top commercial embroidery machine are total game changers as they are able to produce products in bulk without getting tired and with tremendous accuracy.
These machines, however, cannot be run on pixel-based information. Therefore a vector file is required to provide them with an ample amount of instructions to deliver the correct output.
· General Graphical Design
Another method to use vectors is to create general graphical designs. Due to their flexibility and versatility, vector images are able to offer surgical precision without any shortcomings. This is precisely why many logo designers and drawing experts use vector files to facilitate themselves and their clients.
· Creating Animations
If you want your animation to run smoothly, then you again require vector images that can be run using HTML or Adobe Flash.
· High-Quality Prints
Since vector files and graphics retain their image quality and do not lose their crispiness, they are also considered ideal candidates to create superb quality prints. These can even be used on billboards and other types of Out-of-Home advertising such as point of sale displays, ambient media, guerrilla advertising, street furniture, and much more.
When Not To Use Raster Graphics
Where there is a “do”, there has to be a ‘don’t,’ that is why we would like to share with you some advice to help you understand the limitations of each graphic type. So let’s take a look at raster graphics first and see when you need to avoid using them:
- Projection transformation where the location of eye-space points are expressed relative to the projection plane. Using raster images will be quite time consuming, unless you make use of unique algorithms.
- In cases where you would like to retain the sensory perception of your media, raster images may cause a unique loss of information due to the use of large cells to reduce data volumes.
- Similarly, raster maps are cruder in nature, whereas line maps are considerably more beautiful.
When Not To Use Vector Graphics
Likewise, vector graphics can also be questioned even though they are compact, help produce accurate results, lighter data-intensive, more comfortable to manage, and offer fast processing. Here are some of the times where you should avoid them:
- Digital photography or when creating images because vector images have limited colour shading and depth variation, whereas raster graphics can go up to 16 million colours.
- With many images on the web still falling under the 72-100 dpi (dots per inch) range, raster images may look better than vector ones.
- Vector image files that contain text can be tricky to edit when working with EPS and AI files. Images with text saved under the file formats GIF, JPG, and PNG may not reopen for editing.
Final Verdict
In our conclusion, we would like to state that both raster images or graphics and vector images or graphics have their own pros and cons. Raster graphics are composed of pixels, and their refresh process does not depend on the complexity of the picture.
On the other hand, vector graphics are composed of paths as discussed earlier, and their display may flicker if the numbers of primitives within the image are too large. While vector graphics allow you to draw continuously with smooth lines, raster graphics draw with the help of pixel approximation.
Raster graphics are less costly, whereas vector graphics can be more costly comparatively. Raster graphics may occupy lots of space depending upon the quality of the image, while vector graphics do not. This is due to the fact that vector images are not resolution-dependent.
Thus, if you view a vector image, you will find that it has no fixed resolution. Instead, it will be able to show you the resolution of whatever display device you are currently using. In short, some vector files may be viewed as more efficient and versatile due to their nature and other characteristics.
However, these opinions are not universal as each situation and condition is different and unique. You need to be able to convert vector graphics into raster graphics and vice-versa, depending upon your requirements.
Join The Logo Community
We hope you enjoyed When Should You Use Vector or Raster Graphics?. If you would like more personal tips, advice, insights, and access to our community threads and other goodies, join me in our community. You can comment directly on posts and have a discussion.
*TIP – We use and recommend DesignCuts for all your fonts, mockups and design bundles.
 Author Bio
Author Bio
Claudia Jeffrey is a Content Strategist at Crowd Writer, an excellent platform for dissertation service. She likes to read and write about her interests that include graphic designing and modern techniques used to offer innovative solutions for advertising industries. She is an avid fan of all types of anime.


